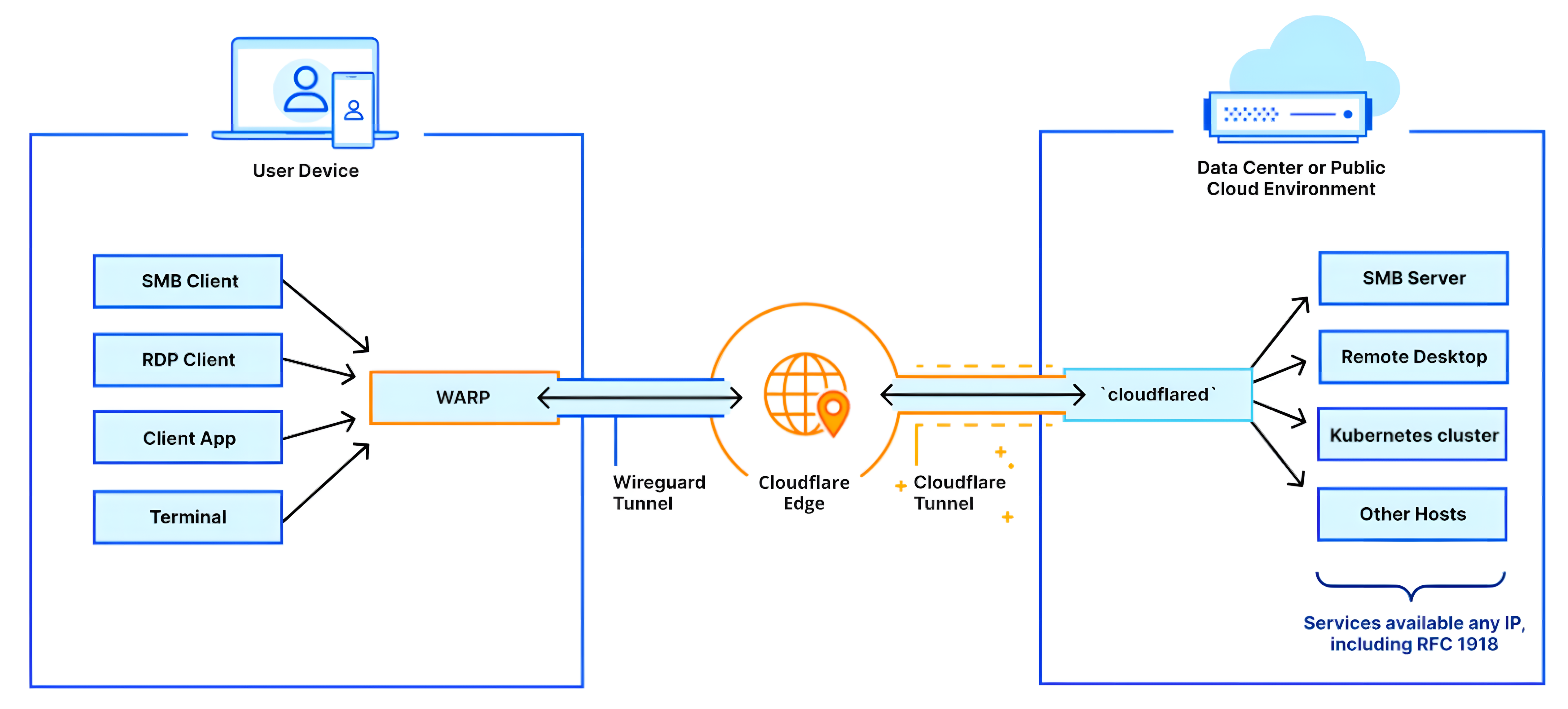
Software-Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN)
Cloud Access Software-Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN) provides a modern deployment model for organizations with multiple branch locations, allowing them to securely connect to a private WAN using public broadband options such as Fiber, Cellular, Fixed Wireless, Cable, and xDSL.
With Cloud Access SD-WAN Orchestrator, branches can be seamlessly integrated into the WAN, managing networking rules between sites. This enables users at one branch to access resources from other branches across different subnets effortlessly.
SD-WAN Topology
Say goodbye to traditional switch-driven WAN designs. SD-WAN is built to connect multiple branch locations, remote workers, mobile offices, and distant users across the globe via broadband connections. It empowers users to access remote applications hosted in public or private clouds, improving application performance and management for SaaS services such as UCaaS and Office 365.
How SD-WAN Works
CloudAccess SD-WAN technology uses an integrated controller to intelligently manage and direct traffic across the WAN. By optimizing traffic routing, it ensures users experience improved application performance across all branch locations. Each branch can leverage multiple internet connections for redundancy and bandwidth, along with advanced features such as quality of service (QoS) for application prioritization and encryption for secure data transmission.
The outcome? Enhanced business productivity, greater efficiency, and reduced IT costs.
Software Defined Wide Area Network – Alternative to MPLS
“MPLS will always have its place for organizations with specific network requirements. It is particularly useful for delivering legacy WANs but can be expensive for small businesses. SD-WAN eliminates the need for dedicated line routing and instead uses software to determine the best paths for traffic over cost-effective broadband connections.
Analytics galore: Network alerts and link health monitoring
Cloud Access is the key to understanding your customers’ needs while providing real-time insights into site performance.
SD-WAN is a great alternative to MPLS because management and deployment can be configured remotely.
- Change routing rules at single or multiple sites within minutes
- Utilize cost-effective hardware at customer locations
- Leverage existing broadband connections at each branch
- Ensure secure WAN access in remote areas
- Implement Quality of Service for broadband
- Enhance bandwidth at branch locations with bonded internet connectivity
- Provide backup internet connectivity through cellular networks such as 3G, 4G, LTE, and 5G
Why offer Cloud Access Software Defined Wide Area Networks?
Until recently, the benefits of SD-WAN were primarily available to enterprises and Fortune 500 companies. We believe that these advantages should not be limited to those with substantial resources. Cloud Access offers a white-labeled SD-WAN platform that enables independent providers to offer SMBs and remote work clients a range of network options.
Cloud Access is a white-label SD-WAN solution, allowing providers to rebrand the service. It operates within the provider’s infrastructure, utilizing their own IP blocks, and can run on x86 hardware with various processors and cost levels. ISPs have the option to source their own hardware or purchase equipment from Soft viewer India to manage costs.
Benefits of Cloud Access
- White Label – Brand it as your own
- Resides within the provider’s infrastructure
- Affordable hardware options
- Zero-touch deployment
- Remote configuration and management
- Bonded Internet Connectivity for increased bandwidth
- Backup Internet Connectivity for high availability
- Site-to-site encryption
- Quality of Service for critical applications